Executive Summary
Embodied AI is central to modern autonomous driving systems. These systems do not merely perceive the environment; they reason, decide, and execute actions in the physical world. This tight coupling between intelligence and actuation significantly raises the safety bar. Errors are no longer abstract model failures but real-world hazards.
Recent real-world incidents, including widely circulated examples involving highly advanced autonomous vehicles such as Waymo, highlight a critical truth: even state-of-the-art systems can fail in rare, ambiguous, or poorly anticipated scenarios. These failures are not necessarily due to a lack of intelligence but to gaps in scenario coverage, uncertainty handling, and system-level validation.
This document highlights the importance of simulation-based testing for identifying and mitigating these perils, how it complements real-world testing, and how a simulation-driven safety strategy can systematically reduce risk in autonomous driving systems.
The Perils of Embodied AI in Autonomous Driving
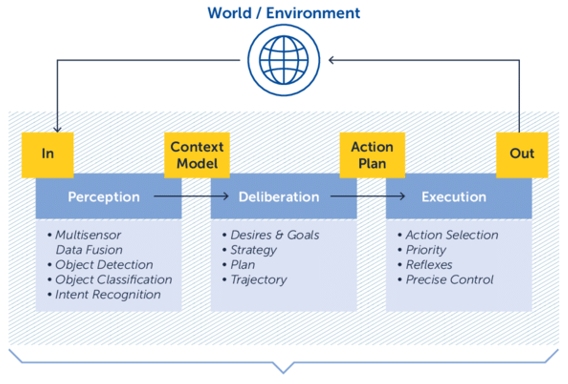
Image source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Sense-Plan-Act-Loop_fig1_358143172
Unlike traditional software systems, embodied AI operates under three compounding constraints:
- Open-World Uncertainty
The real world is not closed or enumerable. Traffic behaviour, human intent, environmental conditions, and infrastructure anomalies often deviate from training data assumptions. - Tight Perception–Action Loop
Errors in perception propagate directly into control decisions. Small misinterpretations can lead to disproportionate physical outcomes. - Long-Tail Safety-Critical Scenarios
The most dangerous situations are often rare, context-specific, and statistically underrepresented in real-world driving logs.
The challenge is not average-case performance, but “robustness under edge conditions”.
A Real-World Illustration: Lessons from Waymo
Publicly shared videos of autonomous vehicles' “misbehavior on roads”, including recent Waymo incidents, demonstrate a recurring pattern in autonomous system failures:
- The system behaves correctly for extended periods.
- A rare interaction or ambiguous situation emerges.
- The vehicle enters a locally valid but globally unsafe behavior pattern.
- A rare interaction or ambiguous situation emerges.
These scenarios often involve:
- Unusual human behavior
- Conflicting environmental cues
- Partial or degraded sensor inputs
- Edge-case interactions between planning and control modules
Such events are extremely difficult to capture through real-world testing alone due to their rarity and unpredictability. Yet they are precisely the scenarios that define public trust and regulatory acceptance.

Image source: https://futurism.com/advanced-transport/waymo-police-standoff
Limits of Real-World Testing for Embodied AI Systems
While on-road testing is necessary, it has fundamental limitations:
- Low yield of rare events: Millions of kilometers may be required to observe a single critical edge case.
- Ethical and safety constraints: Dangerous scenarios cannot be intentionally reproduced on public roads.
- Slow iteration cycles: Each fix requires redeployment, monitoring, and long validation timelines.
These limitations are especially critical for embodied AI systems, where perception, decision-making, and control are inseparable, and failures directly translate into physical risk.
Simulation as a Safety Multiplier
In the context of embodied AI, simulation serves as a safety instrument rather than an alternative to real-world deployment.
1. Edge-Case Amplification
Simulation allows engineers to deliberately construct and replay:
- Rare pedestrian behaviors
- Unprotected turns under occlusion
- Sensor degradation scenarios
- Multi-agent interaction failures
What may take years to observe in the real world can be generated in hours.
2. Scenario Parameterization and Stress Testing
Rather than replaying static scenarios, simulation enables parameter sweeps:
- Slight variations in speed, timing, and intent
- Environmental perturbations
- Agent behavior uncertainty
This exposes fragile decision boundaries and non-linear failure modes.
Failures can be traced across module boundaries, revealing emergent behaviors that unit tests cannot capture.
Bridging the Simulation–Reality Gap
When simulation is used to validate embodied AI systems, it cannot be treated as a standalone solution. The fidelity gap between simulated and real environments must be actively managed to ensure that safety conclusions remain valid beyond the virtual domain.
Effective strategies include:
- Continuous calibration using real sensor logs
- Physics-aware and causally consistent environments
- Hybrid validation loops combining simulation replay with real-world data
- Probabilistic modeling of uncertainty rather than deterministic assumptions
The objective is not to replace real-world testing, but to ensure simulation remains grounded in physical and behavioral reality.
A Simulation-First Safety Framework
A robust safety strategy integrates simulation throughout the development lifecycle:
- Design Phase
Define safety invariants and operational boundaries. - Training Phase
Expose models to diverse, adversarial, and rare scenarios. - Validation Phase
Quantify failure rates, uncertainty bounds, and recovery behaviors. - Deployment Phase
Continuously feed real-world anomalies back into simulation for regression testing.
This closed-loop approach transforms unexpected road incidents into actionable safety improvements.
Our Work: Applying Simulation to Embodied AI Risk Using Co‑Simulation and Scenario Intelligence
Within our autonomy safety efforts, we focus on co-simulation rather than a single monolithic simulator. this capability has evolved into a co-sim framework that explicitly connects autonomy software, simulation environments, and scenario intelligence in a coordinated loop.
Our focus is not on advancing embodied AI algorithms themselves, but on validating their behavior and safety through structured co-simulation and scenario intelligence.
The intent is not to build yet another simulator, but to create a system-level validation layer that allows embodied AI behaviors to be exercised, observed, and stress-tested under controlled yet realistic conditions.
Co-Simulation for Safety Assessment
To evaluate embodied AI behavior under realistic uncertainty and tight system coupling, we adopt a co-simulation–based validation approach that allows system behavior to be exercised under controlled yet physically and behaviorally realistic conditions.
- A production-grade AI End-to-End autonomy stack One or more physics- and sensor-aware simulation environments
- A scenario and orchestration layer that controls agents, environment dynamics, and perturbations
Each component evolves independently but is time-aligned and behaviorally coupled. This allows failures to emerge naturally from system interaction rather than being artificially injected.
 Scenario Intelligence Layer
Scenario Intelligence Layer
At the core of the framework is a structured scenario layer:
- Scenarios are behavioral abstractions, not fixed recordings
- Parameters such as timing, intent, occlusion, compliance, and sensor quality are explicitly modeled
- Variants are generated systematically to explore decision boundaries
This enables targeted exploration of the long tail rather than random simulation at scale.
Integration with the Accident Database
The accident database acts as a grounding mechanism for scenario design.
Instead of replaying accidents verbatim, real-world incidents are:
- Analyzed to extract causal patterns and interaction structures
- Translated into parameterized scenario templates
- Used to prioritize simulation coverage based on real-world risk frequency and severity
This ensures simulation effort is guided by empirical evidence rather than intuition alone.
From Public Incident to Regression Scenario
When incidents are observed—whether from public sources, customer data, or internal testing, the workflow is:
- Identify the interaction failure (not just the outcome)
- Abstract the scenario into actors, constraints, and uncertainties
- Encode it as a parameterized co-simulation scenario
- Execute large-scale variant sweeps
- Capture failures as permanent regression tests
This process converts isolated events into reusable safety knowledge.
Why This Matters
By combining co-simulation with accident-derived scenario intelligence:
- Rare but critical behaviors are systematically exposed
- Planner brittleness becomes measurable
- Safety validation scales without increasing real-world risk
The result is a framework that is neither generic simulation nor overly prescriptive testing, but a practical bridge between real-world incidents and autonomy system validation.
Conclusion
Embodied AI brings unprecedented capability to autonomous driving, but also unprecedented responsibility. Real-world incidents, including those involving industry leaders, reinforce a critical lesson: intelligence alone is not enough.
Simulation provides the only practical means to explore the long tail of risk before it manifests on public roads. When tightly integrated with real-world data and probabilistic safety reasoning, it becomes the backbone of trustworthy autonomous systems.
In the future of autonomous driving, simulation will not be optional. It will be essential.
While on-road testing is necessary, it has fundamental limitations:
- Low yield of rare events: Millions of kilometers may be required to observe a single critical edge case.
- Ethical and safety constraints: Dangerous scenarios cannot be intentionally reproduced on public roads.
- Slow iteration cycles: Each fix requires redeployment, monitoring, and long validation timelines.
These constraints make it impractical to rely on real-world driving alone as the primary safety validation mechanism.
Ready to accelerate your go-to-market timeline while reducing physical risk?
Write to us and talk to our engineering team to see our co-simulation framework in action: sales@vayavyalabs.com
