February 12, 2026 -
With CAN XL, Bosch underlines its central and leading role in the development and implementation of the Controller Area Network (CAN). Originally developed by Bosch in the 1980s, it has become the backbone of in-vehicle communication and is a key element of modern electronic architectures. Ever since, Bosch has remained a key driver of CAN technology and continues to play a leading role in its evolution toward higher performance and flexibility.
The journey of CAN is two-laned: the transceiver performance and the protocol itself. In 1990, the first CAN CC (Classic CAN) devices were introduced. By 2016, CAN FD (Flexible Data Rate) became available, supporting data rates up to 2 Mbit/s with the CAN FD transceiver. Three years later, new Signal Improvement Capability (SIC) transceivers enabled bit rates of up to 8 Mbit/s, further enhancing data throughput and reliability.
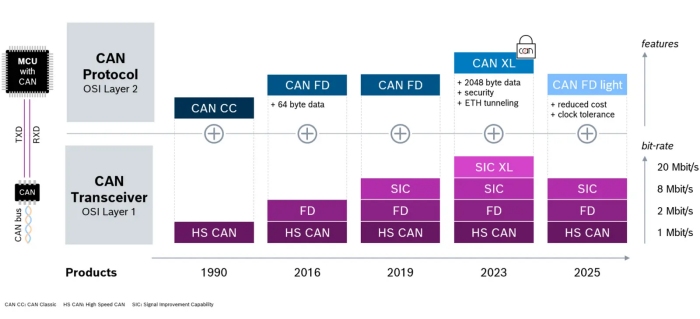
Figure 1: CAN evolution from 1990 to 2025
In 2023, CAN XL marked the next milestone, developed to bridge the performance gap between CAN FD and 100Base-T1 Ethernet. At the time, automotive OEMs relied mainly on CAN FD with 2 Mbit/s and 100 Mbit Ethernet networks. CAN XL complements these technologies by offering a cost-efficient ≤ 20 Mbit/s solution that maintains classic CAN advantages such as arbitration, robustness, and long stub lengths, while introducing enhanced safety and security features, improved quality of service, and the ability to support service-oriented architectures (SOA). CAN XL can be used with all transceivers (CAN HS/FD/SIC). With the latest CAN SIC XL transceiver, it can achieve 20 Mbit/s.
This progression illustrates how Bosch is continuously advancing the CAN ecosystem, uniting proven reliability with modern bandwidth requirements for next-generation vehicle architectures.
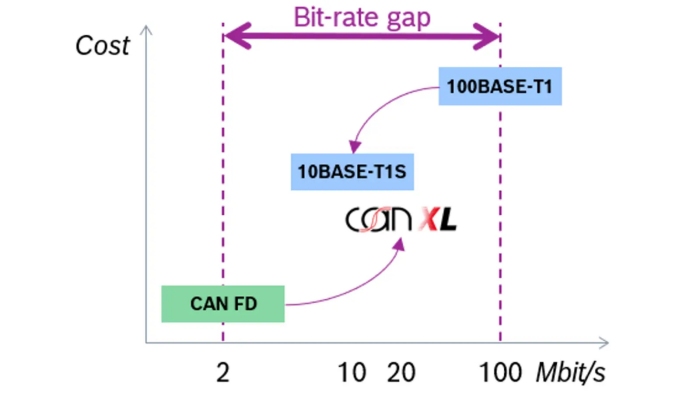
Figure 2: CAN XL was developed to bridge the performance gap between CAN FD and 100Base-T1 Ethernet.
CAN XL includes both the physical hardware and the communication protocol.
The transceiver is the hardware interface to the physical bus line. It converts digital signals from the controller into electrical signals and makes it possible to send and receive CAN XL messages. Bosch develops and supplies these transceivers as part of its hardware portfolio. The latest NT156 transceiver supports bit rates up to 20 Mbit/s.
Bosch develops and licenses IP cores for CAN XL controllers, which are integrated into microcontrollers and ASICs. The XS_CAN is Bosch’s latest CAN XL IP module. It significantly reduces the footprint required for CAN XL implementations, making it ideal for compact devices or large SoCs with multiple CAN interfaces. With only 1-2 KB of local memory, it enables efficient, cost-effective system architectures.
The CAN XL protocol defines how communication takes place, including message formats, error handling, and arbitration. It ensures reliable data exchange across all devices connected within a CAN XL network. The protocol is standardized in ISO 11898-1:2024.
CAN XL enables cost-optimal E/E architectures by providing a single bus for three types of traffic (CAN FD, CAN XL, and Ethernet) within a single network topology. With data rates of up to 20 Mbit/s, it achieves a balance between speed, cost, and network complexity. CAN XL can be used with all CAN transceivers, including HS-CAN, CAN FD, SIC, and SIC XL, which simplifies integration into existing systems.
A large payload capacity up to 2,048 bytes offers sufficient space for virtually any application, while Ethernet tunneling enables the transmission of higher-layer protocols such as TCP/IP or SOME/IP. This allows seamless integration of service-oriented communication into CAN-based networks. Furthermore, CAN XL supports incremental upgrades, allowing CAN FD and CAN XL nodes to coexist on the same network (up to 8 Mbit/s). Its scalability makes it adaptable to various use cases, from cost-sensitive applications to high-performance domains.
These features ensure that CAN XL maintains traditional CAN strengths such as arbitration, robustness, and tolerance for long stubs, while extending its scope toward SOAs and next-generation data services. With the broad availability across automotive microcontrollers, CAN XL is positioned to become a cornerstone of future in-vehicle communication systems.
 "Bosch is committed to technology, knowledge transfer, and CAN XL – through publications, presentations, and collaboration both within and beyond the automotive industry. Bosch works together with the CAN in Automation (CiA) association, which drives the development of the CAN XL standard, thereby contributing to the establishment and standardization of this next-generation CAN technology." Andreas König, Director Product Management Intellectual Property
"Bosch is committed to technology, knowledge transfer, and CAN XL – through publications, presentations, and collaboration both within and beyond the automotive industry. Bosch works together with the CAN in Automation (CiA) association, which drives the development of the CAN XL standard, thereby contributing to the establishment and standardization of this next-generation CAN technology." Andreas König, Director Product Management Intellectual Property
Modern radar sensors generate large data volumes that must be exchanged across vehicle domains in real time. Accurate time synchronization is critical for consistent interpretation of object and target data. The XS_CAN IP integrates hardware-based timestamping with a resolution up to 64 bit/s, enabling precise temporal alignment across multiple radar nodes.
Compared to Ethernet solutions such as 10Base-T1S, CAN XL offers a cost-efficient alternative. It supports various transceiver options such as CAN, CAN SIC, and CAN SIC XL with scalable node configurations. With bandwidths up to 8 Mbit/s using CAN SIC transceivers, CAN XL provides 84 % higher bandwidth than CAN FD at the same physical-layer cost. With the new CAN SIC XL transceivers, the difference is even bigger: +340% more bandwidth than CAN FD. Network simulations show that CAN XL can handle up to 4,000 location entries (20 bytes each) at 77 % bus load or 1,400 radar objects (60 bytes each) at 83 % bus load within 50 ms.
In addition, CAN XL supports Ethernet frame tunneling for Diagnostics over IP (DoIP), combining high bandwidth, flexibility, and cost efficiency. This makes it a future-ready solution for radar-based automotive applications.
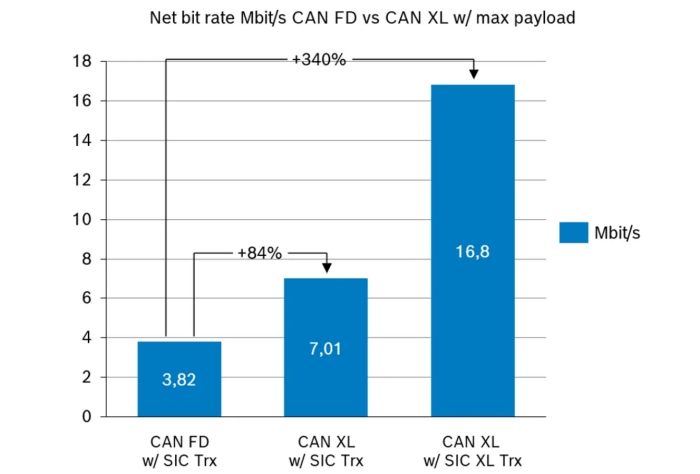
Figure 3: Differences in bandwidth between CAN FD and CAN XL
From the first CAN prototype to the latest CAN XL generation, Bosch has consistently advanced the standards of in-vehicle communication. Together with other industry partners, Bosch is also driving the development of the CANsec standard (a layer-2 security protocol) within the CiA (CAN in Automation), which is essential for secure SDV architectures. This long-term commitment to performance, interoperability, and reliability not only defines the evolution of the CAN ecosystem but also reinforces Bosch’s reputation as a technology leader and trusted partner for future vehicle architectures. With CAN XL, Bosch once again demonstrates how established strengths and forward-looking solutions can merge into a powerful foundation for the next era of connected mobility.